Submitted by ETC Staff on
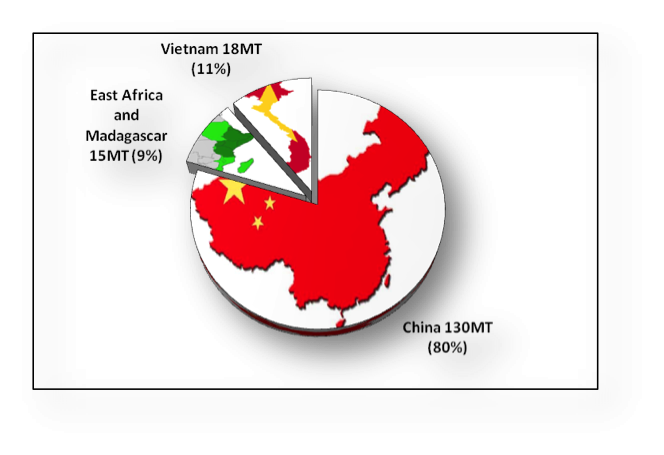
This case study illustrates developments in synthetic biology that could be disrupting the livelihoods of thousands of small farmers who cultivate Artemisia for the plant’s anti-malarial compounds. These developments impact the sustainable use of biodiversity and fair and equitable sharing of benefits from the genetic resources that produce natural plant products. If biosynthesis of artemisinin can be successfully scaled up, the pharmaceutical industry will source future supplies of artemisinin from a handful of microbial cell factories instead of farmers in Asia and Africa.
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 1.02 MB |